Coxarthrosis(Arthrosis of the hip joint) is a type of deforming arthrosis of the joints, which is a chronic non-inflammatory disease that affects the hip joint (one or both at the same time). This disease has a degenerative-dystrophic character. This means that the cartilage that makes up the hip joint undergoes degenerative changes, and the surfaces of the bones also change. In addition, bone formations (osteophytes) are formed, the joint is deformed, the range of motion in the affected joint decreases, and they become extremely painful and uncomfortable.
The hip joint is one of the largest joints in our body. It is thanks to it that the motor function in the human body is very important and it is also responsible for making our body move. If the hip joint gets sick, then it affects the whole body and prevents a person from living peacefully, walking, not to mention sports. Very often we see elderly people who are forced to rely on a cane due to hip joint disease.
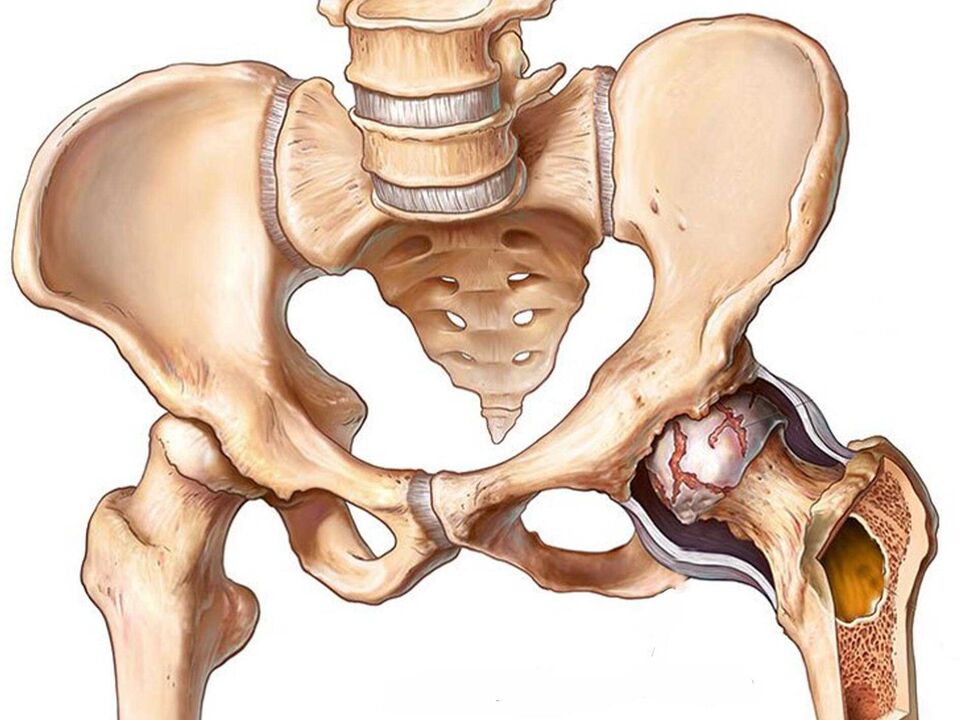
Although the hip joint is extremely massive and strong, at the same time it is quite vulnerable, especially over time. Hip joint pain significantly reduces a person's quality of life.
Coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint)It firmly takes the second place among arthrosis of the joints after gonarthrosis (arthrosis of the knee joint) in the frequency of diagnosed cases.
Classification of coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint)
It happensCoxarthrosisBoth primary and secondary.
- Primary coxarthrosis is mainly caused by the inevitable wear and tear of the hip joints throughout life and usually affects people after the age of 40.
- The causes of secondary coxarthrosis are usually the following diseases: congenital dislocation of the hip, necrotic masses of the femur in the head, Peter's disease, traumatization of the anterior hip joint, inflammatory diseases of the hip joint. whereArthrosis of the hip jointIt can affect one joint alone, or both.
There are several types of coxarthrosis:
- Dysplastic (congenital pathology and characterized by underdevelopment of the joint).
- Involute (typical for older people and associated with age-related changes).
- Post-infectious (it was preceded by purulent or purulent-allergic, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Illness due to Peter's disease (development of osteochondropathy in the hip area).
Coxarthrosis Due to trauma (neck and skull fractures (femur)).- Coxarthrosis due to metabolic disorders (metabolism).
- Dyshormonal (long-term use of glucocorticosteroids, antidepressants).
- idiopathic (the cause of which could not be determined).
Symptoms of coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint)
In order to correctly describe the symptoms of coxarthrosis, we must take into account the stages of the disease at the same time, because the symptoms depend on the stage of the disease.
Stages of coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint)
In general, there are three stages of coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint):
- 1st stage of coxarthrosis. This is the initial stage of the disease, during which the symptoms are still mild. The joint does not hurt much at this stage and the pain appears only after physical exertion, such as lifting heavy objects or running, hiking long distances. After a person rests, the pain disappears. The patient may also develop lameness if, for example, he walks more than two kilometers. Increases pain when climbing stairs. The motor volume of the joint is slightly reduced or preserved. X-ray examination can show only small changes in bone structures.
- 2nd stage of coxarthrosis. This stage develops in the absence of treatment of the first stage. A specific joint crack (cramp) is added to the above symptoms. The pain becomes more intense and begins to spread to the groin, and may also spread to the thigh and knee. At this stage, not only strong, but any movement can cause pain symptoms, even a small load on the hip joint. Even getting out of bed or turning your body can cause pain. There is a tension in the periarticular muscles that does not go away even at night, so patients often complain that the thigh hurts at night. A person may start limping even after a short walk (up to 500 meters). At this stage, the disease already forces a person to rely on a cane while walking. The limitation of movement in the joint becomes more pronounced. According to the results of X-ray diagnostics, the generated osteophytes are determined.
- 3rd stage of coxarthrosis. the last stage of the disease. At this stage, the pain becomes constant and bothers the patient. Any movement, even the weakest, increases pain symptoms several times. At this stage, the hip joint is completely immobilized. The muscle mass of the hips and buttocks decreases due to muscular dystrophy, which is very noticeable. It is characteristic that the patient cannot stand straight, and the body will be bent. Any arthrosis leads to the formation of a contracture (bent position), in which case the contracture is also formed due to the fact that the muscle fibers are in constant tension, and the lateral leg of the leg becomes shorter. As a result of immobilization of the hip joint, the whole leg stops performing motor function, which has a very negative effect and causes osteochondrosis damage. In addition, the spine suffers, discomfort and pain appear in the sacral area.
Causes of coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint)
The main causes of coxarthrosis:
- Age-related changes in the joint. typical for older people. The hip joint wears out over time, ceases to perform its functions over time, "drying out", which causes a decrease in its shock absorbing function and the friction of the bones that make up the joint against each other.
- Hip joint injury. The most common injury in this age group is a fracture of the femoral neck, which can be disabling if not treated properly. Joints can be damaged at any age, but older people suffer more.
- Disturbed metabolism. This is typical for people who have a history of metabolic disorders and diseases related to metabolic disorders.
- Violation of hormonal status. It is more common in women, especially those who have been taking antidepressants and glucocorticosteroids for a long time.
- Hereditary anomalies in the development of the locomotor system, as well as congenital anomalies. Unfortunately, nowadays quite a large number of children are born with congenital pathologies of the muscular and nervous system. As for the anomalies of the development of the hip joint, it can include its dysplasia, in which several structures of the joint do not develop.
- Systemic arthritis. Damage to several joints can also lead to damage to the hip joint. In this case, one of the main risk factors will be the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Rheumatic diseases and chronic arthritis. All these can also cause pain in the hip joint. Such diseases that cause pain in the studied joint include: rheumatism; rheumatoid arthritis; spondyloarthropathy; Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
- Defeat of osteochondrosis. Osteochondrosis of the spinal column is a fairly common and serious disease, which, in addition to the spine, can "disable" other structures of our body, in particular, the hip joint.
- Joint muscles and ligaments. Damage to these structures can also be the result of degenerative and dystrophic processes in the hip joint.
- Infectious damage to both the joint itself and the hip. Such injuries are very serious because they cause serious consequences and are sometimes difficult to treat. Osteomyelitis may develop, which simply "eats" or "removes" bone tissue. Tuberculous lesions can also occur, and more often such localization occurs in children of the prepubertal period. An abscess in the pelvic area, which is more often the result of an untreated or poorly treated infectious process, for example, with appendicitis, inflammatory processes, especially when it comes to the female genital organs (ovarian disease), the development of an abscess. In the area of ischiorectal deepening, which causes walking disorders (appearance of lameness). In most cases, pain and lameness are the result of compression or damage to the surrounding nerves (sciatic or obturator).
- Malignant neoplasms. Quite rarely, malignant neoplasms affect the hip joint and its surrounding bones, because more often the cause of the disease is metastases from other malignant areas, for example, breast or lung cancer.
- Narrowing of the lumen of the aorta and iliac arteries (their stenosis and occlusion). At the same time, the joint receives less and less nutrients for normal functioning, which leads to its degeneration.
Coxarthrosis risk group (arthrosis of the hip joint)
The main risk group may include the following categories of people and harmful factors:
- Different people. This disease is characteristic of older people, the elderly, because degenerative processes occur that occur precisely in this age period.
- a womanAccording to statistics, women are more prone to hip joint problems.
- Overweight or obese people.
- Previous trauma to one or both hip joints.
- Hereditary predisposition to this kind of diseases and congenital anomalies in the development of the hip joint.
- The presence of infectious lesions in the past, such as abscesses, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, osteomyelitis, etc. Sh.
- heavy physical labor.
- Summer residents who have an extremely high risk of developing coxarthrosis.
Prevention of coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint)
The main measures for the prevention of coxarthrosis are as follows:
- Dosed physical activity. It is important to do gymnastics and rotate the joint in order to prevent the development of pathological processes in it and slow down its aging. This will help to improve the condition of not only the hip joint, but also the whole body.
- If there are metabolic disorders, they must be corrected. For this you need to contact a specialist.
- Watch your weight. Do not forget that the hip joint already carries a large load, almost the entire body, so you should not interfere with it to perform its functions. In addition, a large weight will put so much pressure on the joints that they will gradually break. Overweight people are also prone to metabolic disorders.
- Avoid sudden body turns, especially if you are not warmed up and ready, this will prevent you from injuring your femoral head and neck.
- It is better, of course, to choose a sport in which joint damage is least dangerous, such as swimming or yoga, especially if there is a hereditary predisposition or developmental anomalies.
- Susceptibility to joint diseases implies careful treatment of them, as well as regular visits to the doctor, so as not to miss the possible development of joint disease or any other pathological process.
- If a child is diagnosed with hip dysplasia, treatment should be done immediately! It is better for a child to be immobile for a few weeks at an early age than to suffer for the rest of his life.
- Timely treatment of infectious diseases, especially those that threaten to spread to the hip joint.
Diagnosis of coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint)
When diagnosing coxarthrosis, it is very important to find its cause. After all, as discussed above, there are many reasons, they are diverse andTreatment of hip osteoarthritisTherefore, it is radically different. Sometimes it is not so easy, and sometimes it is impossible at all. Emphasis is placed on studying the manifestations of the disease and selecting the appropriate treatment.
First of all, the doctor carefully examines the patient, studies in detail the complaints, the causes of the disease, hereditary load, the presence of injuries, etc. Sh. The complaints described above and how long they have been observed in the patient are very important.
After the interview, the doctor personally examines the affected area for inflammatory changes, trophism, deformation, limb shortening, asymmetry, etc. Sh. And children may have "clicking" symptoms.
Additional examination methods - computerized and magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound and X-ray examination - are an important moment, because they will help you make a final diagnosis. Differential diagnosis of coxarthrosis from other diseases of the hip joint, this point is extremely important.















































